A team of researchers from South Korea has developed an innovative anode-free lithium metal battery that could nearly double the driving range of electric vehicles (EVs) without increasing the size of the battery. This breakthrough could significantly enhance the practicality of EVs, particularly for long-distance travel, allowing a vehicle to travel from Seoul to Busan and back on a single charge.
The anode-free battery technology addresses a major concern for EV users: battery performance. Currently, many electric vehicles experience reduced efficiency and range in colder weather, which can deter potential customers. The new battery design aims to mitigate these issues, promising a more reliable and efficient power source regardless of external conditions.
Technical Advancements and Implications
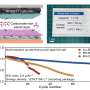
The research team focused on utilizing lithium metal as a key component. Traditional lithium-ion batteries rely on a combination of lithium and an anode to store energy. By eliminating the anode, the new battery design not only increases the energy density but also enhances the overall performance of the battery. As a result, this technology could pave the way for longer driving ranges, a crucial factor for consumers considering the switch to electric vehicles.
According to the research findings, the anode-free battery can achieve nearly double the energy density compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. This could mean that an electric vehicle equipped with this new technology might be able to travel distances previously thought unattainable on a single charge.
Moreover, the implications of this development extend beyond just extending driving ranges. It may also lead to reduced charging times and improved battery lifespan, further improving the overall user experience for EV drivers.
Future Prospects and Market Impact
As the automotive industry continues to shift towards electrification, innovations such as the anode-free battery could play a pivotal role in making electric vehicles more appealing to a broader audience. The increased range and performance might help alleviate consumer anxieties regarding battery life and charging infrastructure, which are often cited as barriers to EV adoption.
The Korean research team is now exploring partnerships with automotive manufacturers to bring this technology to market. If successful, the introduction of anode-free batteries could disrupt the current landscape of electric vehicle technology.
With the global push for greener transportation solutions, advancements like these are critical. As countries strive to meet ambitious climate targets, enhancing electric vehicle performance can significantly contribute to reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable energy use.
This breakthrough marks a significant step toward a future where electric vehicles are not only more efficient but also more convenient for everyday drivers. The research team anticipates that further developments could lead to commercial applications within the next few years, potentially reshaping the future of transportation.