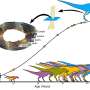
A recent study has unveiled that the iconic Tyrannosaurus rex continued to grow until the age of 40, challenging long-held beliefs about the dinosaur’s maturation timeline. Researchers have utilized advanced techniques to analyze fossilized leg bones, revealing that these massive carnivores did not cease growing at around 25 years, as previously estimated.
For years, scientists relied on counting annual growth rings within the leg bones of T. rex to gauge their age and growth rates. This method, akin to measuring the rings of a tree, provided critical insights into the life cycles of these ancient animals. The study, conducted by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, marks a significant advancement in our understanding of dinosaur biology.
Unraveling the Growth Patterns
The research team analyzed a collection of fossilized leg bones from several T. rex specimens, allowing them to establish a more accurate picture of growth patterns. The findings indicate that these dinosaurs grew steadily throughout their lives, with a significant increase in size occurring well beyond the previously accepted growth cessation at 25 years.
This new evidence suggests that T. rex reached its full size and physical maturity only after decades of growth. It also raises questions about the ecological and evolutionary factors that may have influenced their extended growth periods. The implications of this research could transform how scientists interpret the life history of not just T. rex, but other dinosaur species as well.
The study, published in 2023, reflects ongoing efforts to refine our understanding of dinosaur physiology. Researchers emphasize that the insights gained from examining growth rings are crucial for reconstructing the life histories of these prehistoric creatures, providing valuable data for paleontologists.
Significance of the Findings
The revelation that T. rex could live up to 40 years adds a new dimension to our understanding of dinosaur longevity and growth. It prompts a reevaluation of how these creatures interacted with their environment and their peers over extended lifespans.
With the potential for greater size and strength over time, older T. rex individuals might have had distinct advantages in terms of survival and reproduction. This extended growth period might also suggest complex social structures and behaviors within T. rex populations, as older individuals may have played crucial roles in their ecosystems.
The study’s lead researcher stated, “Understanding the growth patterns of T. rex not only sheds light on their biology but also enriches our comprehension of the ecosystems they inhabited.” This research underscores the importance of integrating modern technologies with traditional paleontological methods to gain deeper insights into the past.
As scientists continue to explore the mysteries of prehistoric life, findings like these enhance our appreciation for the complexities of the natural world. The extended growth timeline of T. rex serves as a reminder of the intricate life histories that shaped the history of our planet.