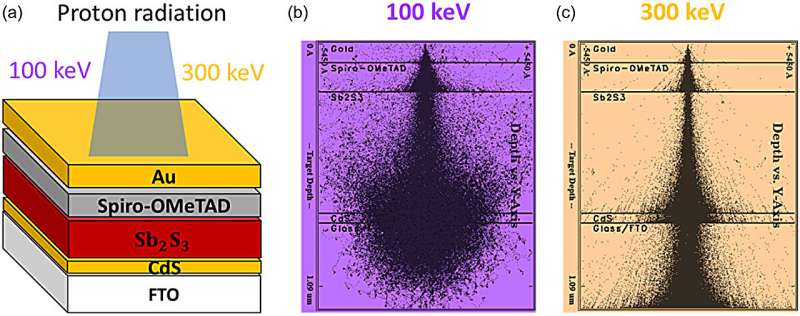
A groundbreaking platform has been developed to evaluate the fairness and accuracy of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms in detecting diabetic eye disease for possible use within the National Health Service (NHS). This innovative testing platform, introduced in September 2023, marks a significant step toward ensuring that AI technologies are implemented in a manner that is equitable and transparent in healthcare settings.
The platform allows for real-world, head-to-head testing of various commercial AI algorithms. By focusing on diabetic eye disease, which affects millions globally, the initiative aims to establish a robust framework for assessing the efficacy of AI tools in medical diagnostics. According to researchers involved in the project, the goal is to determine whether these algorithms can consistently deliver fair outcomes across diverse patient populations.
Ensuring Fairness and Transparency in AI
The need for such a platform arises from growing concerns regarding potential biases in AI systems. In healthcare, where decisions can significantly impact patient outcomes, ensuring that AI algorithms are both accurate and equitable is crucial. Researchers emphasize that the new testing platform will provide insights not only into the performance of individual algorithms but also into how they handle different demographic groups.
The initiative is supported by several prominent organizations, including the National Health Service and various universities across the United Kingdom. These institutions are collaborating to create standards that will guide the evaluation process. By establishing a set of criteria for fairness and transparency, the platform aims to build trust among healthcare providers and patients alike.
Implications for Future AI Deployments
As the healthcare landscape increasingly embraces AI technologies, the implications of this testing platform extend beyond diabetic eye disease. Researchers believe that the methodologies developed here could be adapted for other medical conditions, potentially revolutionizing how AI is integrated into health systems worldwide.
Early results from the platform will be closely monitored and analyzed to gauge its impact on both patient care and the broader healthcare sector. The initiative not only addresses the immediate need for effective AI screening tools but also sets a precedent for future technological advancements in medicine.
With the ongoing evolution of AI in healthcare, stakeholders are hopeful that this testing platform will serve as a model for responsible AI deployment, ensuring that emerging technologies enhance patient outcomes without introducing new disparities. As the initiative progresses, it is expected to draw attention from international health organizations and policymakers, potentially influencing AI regulations globally.
In conclusion, the introduction of this real-world testing platform represents a significant milestone in the intersection of technology and healthcare. By prioritizing fairness and accuracy, researchers aim to pave the way for a future where AI tools are trusted allies in the fight against diseases such as diabetic eye disease.