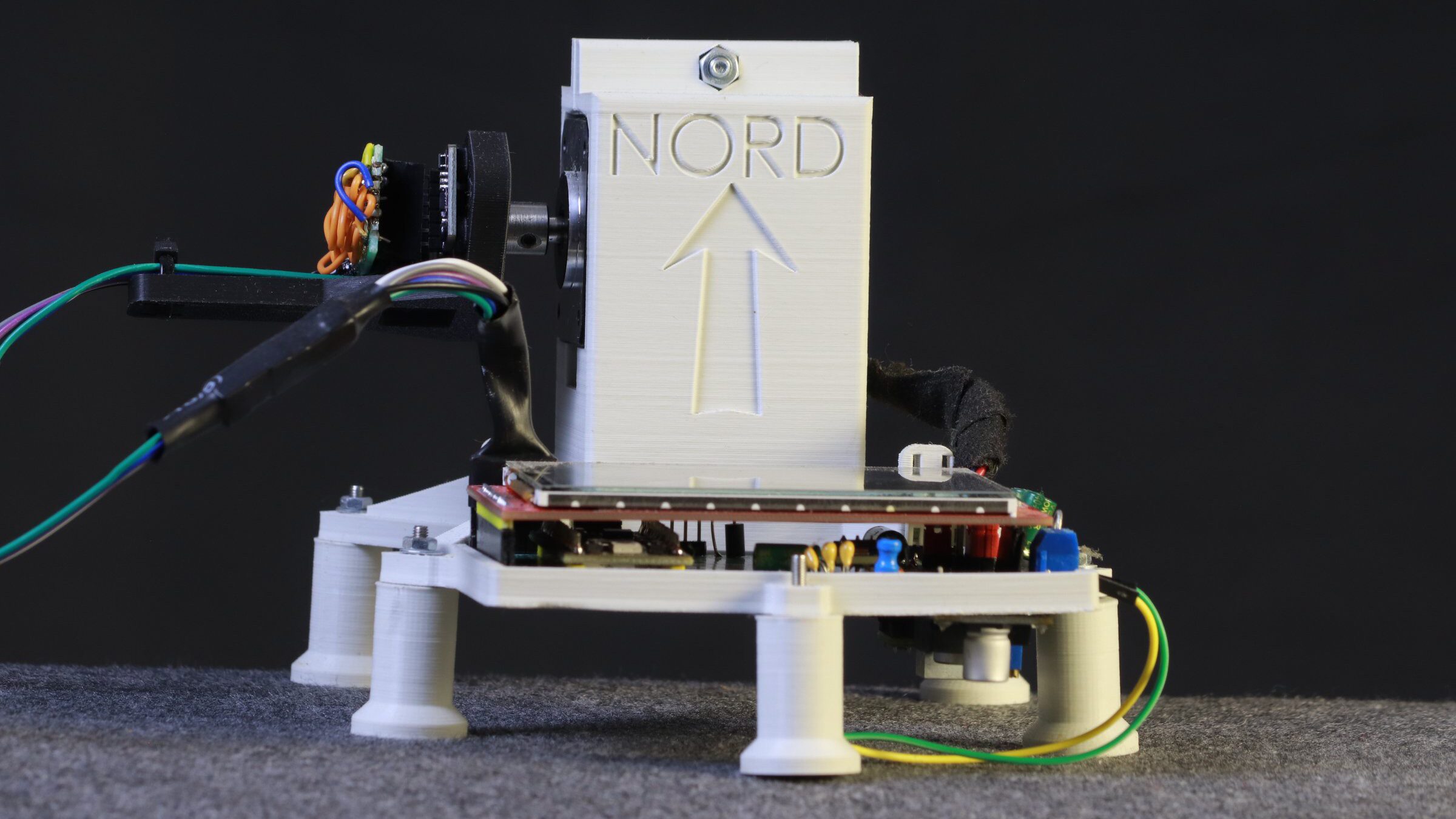
A groundbreaking device created by scientist Bertrand Selva effectively measures the Earth’s rotation using two gyroscopes, a significant achievement in demonstrating rotational motion without relying on traditional methods like the Foucault pendulum. This innovative apparatus incorporates a pair of BMI160 MEMS gyroscopes and offers a unique solution to a long-standing scientific inquiry.
The device operates by detecting the Earth’s rotation, which occurs at approximately 0.00416 degrees per second. The gyroscopes feature a least significant bit for angular velocity of 0.0038 degrees per second, allowing the system to identify the subtle signals associated with Earth’s movement. To achieve accurate measurements amidst various noise factors, the setup includes careful positioning of sensors in four distinct orientations. This process helps neutralize sensor bias and the effects of gravitational forces.
Before conducting tests, Selva aligned the sensors toward true north. The system utilized a stepper motor to cycle the sensors through the four positions, with a Raspberry Pi Pico recording 128 measurements at each orientation. The cycle could be repeated up to 200 times, with the error margin decreasing with each iteration.
To refine the data, a Kalman filter was employed, successfully extracting a signal that came within two percent of the true rotational velocity. Notably, Selva observed that the accuracy of the measurements was significantly influenced by the alignment to true north, to the extent that it could serve as a functional compass.
Although Selva’s impressive demonstration failed to convince a flat-earth believer in his vicinity, the device stands as a testament to innovative thinking in scientific exploration. The simplicity of this system contrasts with other methods of measuring the Earth’s rotation, which can include more complex technologies, such as those used in gaming systems like the PlayStation.
For those seeking higher precision, established standards organizations continue to provide rigorous methodologies for measuring the Earth’s rotation, highlighting the ongoing importance of accurate scientific measurement in understanding our planet’s dynamics.