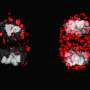
Recent research has uncovered a significant mechanism that influences the fate of T cells in the immune system. Scientists at the University of California, San Francisco have highlighted the role of asymmetric cell division (ACD) in determining whether a T cell becomes a short-lived effector or a long-lived memory cell. This discovery, published in the journal Nature on March 15, 2024, sheds light on a fundamental process that impacts immune responses.
T cells play a crucial role in the body’s defense against infections and diseases. During their division, ACD ensures that each daughter cell inherits different cellular components. This unequal distribution of materials drives the cells toward divergent functions. One daughter cell evolves into an effector T cell, which actively combats pathogens, while the other develops into a memory T cell, responsible for long-term immunity.
The research team utilized advanced imaging techniques to observe T cell division in real time. Their findings revealed that the distinct fates of T cells are not random but rather influenced by specific molecular mechanisms. These mechanisms include signaling pathways and cellular components that guide the cells’ developmental trajectories.
Understanding these processes has profound implications for immunology and therapeutic interventions. The ability to manipulate T cell fate could enhance vaccine efficacy or improve treatments for autoimmune diseases and cancers. By promoting the development of memory T cells, researchers aim to create more robust and lasting immune responses.
The study’s lead author, Dr. Emily Chen, emphasized the importance of these findings. “Our research provides critical insights into how immune cells are programmed during their development,” she stated. “By understanding the intricacies of T cell fate decisions, we can better harness their power for therapeutic purposes.”
This work represents a significant step forward in immunological research. As scientists continue to explore the complexities of T cell biology, the potential for innovative treatments becomes increasingly promising. The findings underscore the importance of basic research in uncovering mechanisms that could lead to groundbreaking medical advancements.
In conclusion, the study conducted by the team at the University of California, San Francisco highlights the intricate processes governing T cell fate through asymmetric cell division. With further exploration, these insights could pave the way for new strategies in immunotherapy and vaccine development, ultimately enhancing the body’s ability to fight off diseases.