Elon Musk has announced a significant shift in SpaceX’s objectives, moving the company’s near-term focus from Mars colonization to establishing a manufacturing facility on the Moon. This decision, communicated during an internal meeting and confirmed in public statements, marks a pivotal moment in the space industry, reshaping SpaceX’s mission since its inception in 2002.
The announcement emerged through various channels, including internal leaks and Musk’s social media. According to Futurism, Musk informed employees that SpaceX would pursue an ambitious lunar development program, which includes constructing a factory capable of processing lunar regolith and extracting resources. This initiative transcends the historical Apollo missions and NASA’s Artemis program, aiming for a long-term industrial presence on the Moon.
The Strategic Shift: Understanding the Motivations
Musk’s pivot towards the Moon appears to be driven by a combination of geopolitical, technological, and financial factors. As highlighted by Interesting Engineering, SpaceX is now in direct competition with China’s rapidly advancing lunar program. The China National Space Administration (CNSA) has accomplished several ambitious robotic missions, including the Chang’e 5 sample return mission, and aims for a crewed lunar landing by 2030, along with plans for a permanent International Lunar Research Station (ILRS).
Control over the Moon is seen as strategically significant, particularly regarding access to vital resources like water ice deposits. Musk, who has increasingly positioned himself at the intersection of private enterprise and government interests, recognizes that the current political climate favors lunar initiatives over Mars exploration in the immediate future. NASA’s Artemis program, despite facing delays, remains a key human spaceflight initiative, and SpaceX is contracted to provide the Human Landing System (HLS) for lunar missions.
A Vision for Lunar Manufacturing
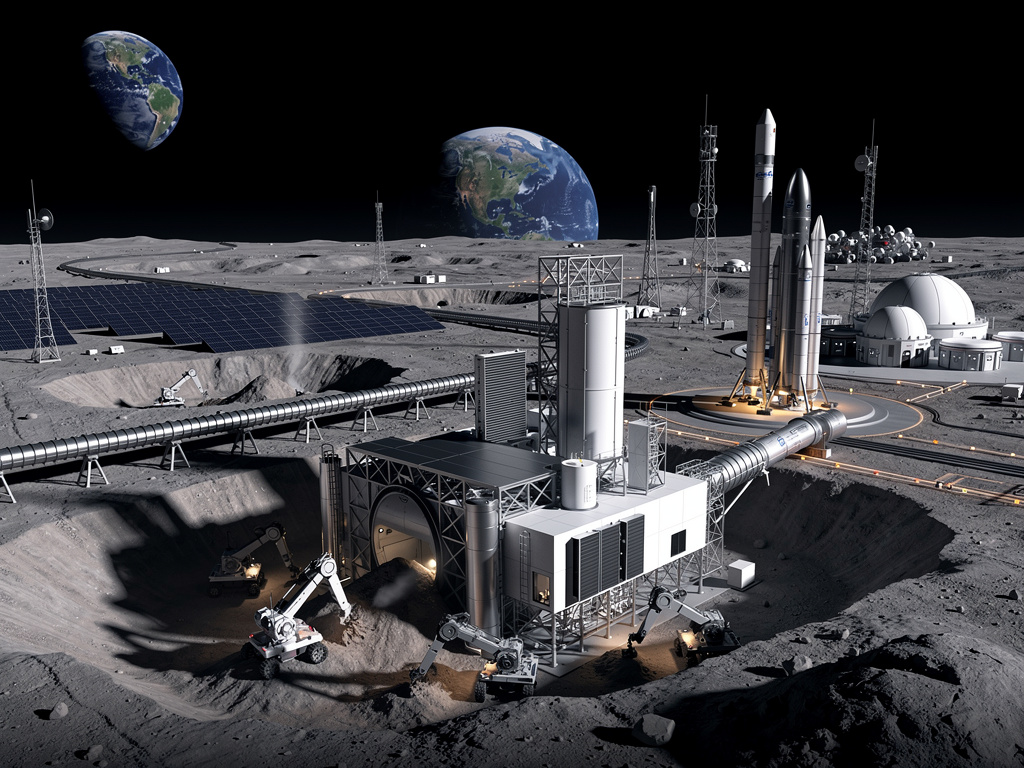
The concept of a lunar factory is a central focus of Musk’s announcement. As reported by Singularity Hub, Musk outlined a phased approach to building this infrastructure, starting with robotic cargo deliveries via SpaceX’s Starship. This would be followed by deploying autonomous construction equipment to process lunar regolith into usable materials.
Lunar regolith, the fine dust covering the Moon’s surface, contains essential elements like silicon, iron, and oxygen, which could be refined using solar-powered technologies. The ability to produce oxygen would be particularly beneficial, serving both as a breathable atmosphere for habitats and as an oxidizer for rocket fuel, thus reducing the cost of return missions to Earth.
The factory would also aim to manufacture solar panels and structural components, with advanced 3D printing techniques tailored for lunar conditions. Space.com notes that SpaceX has been developing in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) prototypes for several years, yet these technologies remain untested in actual lunar environments, presenting considerable engineering challenges.
In a provocative twist, Musk has proposed a lunar catapult — an electromagnetic launch system designed to send payloads from the Moon’s surface into orbit or towards Earth without traditional rockets. This concept, rooted in decades of theoretical research, could revolutionize the economics of space exploration, enabling efficient transport of lunar materials.
Balancing Ambitions and Realities
The question of whether Musk has abandoned the dream of Mars colonization is complex. According to Ars Technica, Musk frames the lunar pivot as a strategic decision rather than a retreat. The Moon will serve as a testing ground for technologies necessary for Mars habitation. Critics, including Robert Zubrin of the Mars Society, express concerns that lunar projects could detract from Mars ambitions, potentially becoming an endless resource drain.
SpaceX’s pivot could alter the competitive landscape of the commercial space sector. Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origin has pursued a Moon-first strategy for years, focusing on developing the Blue Moon lander. SpaceX’s shift could validate Bezos’s approach or threaten Blue Origin’s emerging position in lunar development.
The broader implications of Musk’s lunar ambitions cannot be understated. The competition for lunar resources is intertwined with national security considerations, particularly as China’s space program expands. Musk has acknowledged the necessity of maintaining U.S. leadership in cislunar space, emphasizing the strategic importance of securing lunar resources.
Economic and Logistical Challenges Ahead
The financial and logistical implications of establishing a lunar factory are vast. Current estimates suggest that developing permanent infrastructure on the Moon will require unprecedented investment levels. Analysts are divided on the financial viability of lunar resource extraction, with some believing it could create new markets worth trillions, while others caution about the risks and technological uncertainties involved.
NASA’s response to SpaceX’s plans has been measured. While the agency welcomes the increased focus on lunar development, it is concerned that the ambitious scope of Musk’s vision could complicate NASA’s own gradual approach to lunar exploration. The potential for a private company to build autonomous facilities raises questions about oversight and environmental preservation.
Ultimately, Musk’s plans for lunar development reflect a significant evolution in humanity’s relationship with space. If realized, this vision could redefine industrial activity beyond Earth, with profound implications for resource management, national security, and international law. The Moon, once seen as a barren landscape, is now positioned at the forefront of a new era in space competition, with Musk leading the charge.
As SpaceX prepares to launch its first uncrewed Starship mission to the Moon within the next 18 to 24 months, the world watches closely to see if Musk’s audacious plans can become reality. The stakes are high, and the challenges immense, but the momentum surrounding lunar exploration is undeniable.