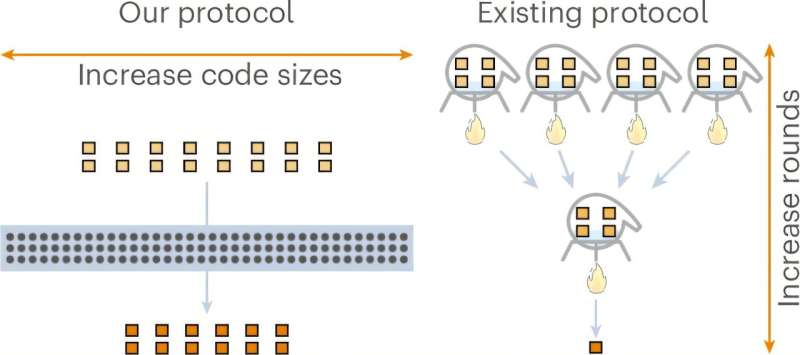
The WB-57, a high-altitude research aircraft operated by NASA, plays a crucial role in atmospheric research. Based in Houston, Texas, this unique aircraft enables scientists to gather data from the stratosphere, contributing significantly to our understanding of climate change and atmospheric phenomena.
Designed for missions that require flying at altitudes of up to 60,000 feet, the WB-57 is equipped with advanced instrumentation. This enables it to conduct scientific experiments and collect data in environments that are otherwise inaccessible. The aircraft’s capabilities make it an invaluable asset for a variety of research initiatives.
Key Functions and Uses
The primary mission of the WB-57 involves studying atmospheric conditions, including the impact of greenhouse gases and ozone levels. By flying above the majority of the Earth’s weather systems, it provides a clearer view of the upper atmosphere, allowing researchers to gather data that is essential for climate modeling.
In 2023, its missions included collaborations with various institutions to investigate the effects of pollution on atmospheric health. The WB-57’s ability to carry specialized equipment, such as sensors for measuring aerosols and trace gases, makes it an ideal platform for these studies.
The aircraft frequently participates in field campaigns, where it operates alongside satellites and ground-based observations. This multi-faceted approach enhances the accuracy of the data collected, providing a more comprehensive understanding of atmospheric dynamics.
Technological Advancements
The WB-57 is not merely a platform for data collection; it also represents significant technological advancements. It can be outfitted with a range of scientific instruments tailored to specific research requirements. This flexibility allows researchers to adapt to changing scientific needs and incorporate the latest technologies in atmospheric science.
Moreover, the aircraft is designed for long-duration flights, which can last several hours. This endurance is essential for gathering extensive data over large geographical areas, enabling scientists to analyze trends and variations in atmospheric conditions effectively.
The ongoing contributions of the WB-57 to scientific research underscore its importance within NASA’s fleet. As climate change continues to pose challenges globally, the data collected from such high-altitude missions is vital for informing policy and guiding future research.
In conclusion, the WB-57 stands out as a sophisticated tool in the realm of atmospheric research. Its operations from Houston not only enhance our understanding of climate-related issues but also demonstrate the ongoing commitment of NASA to advancing scientific exploration.