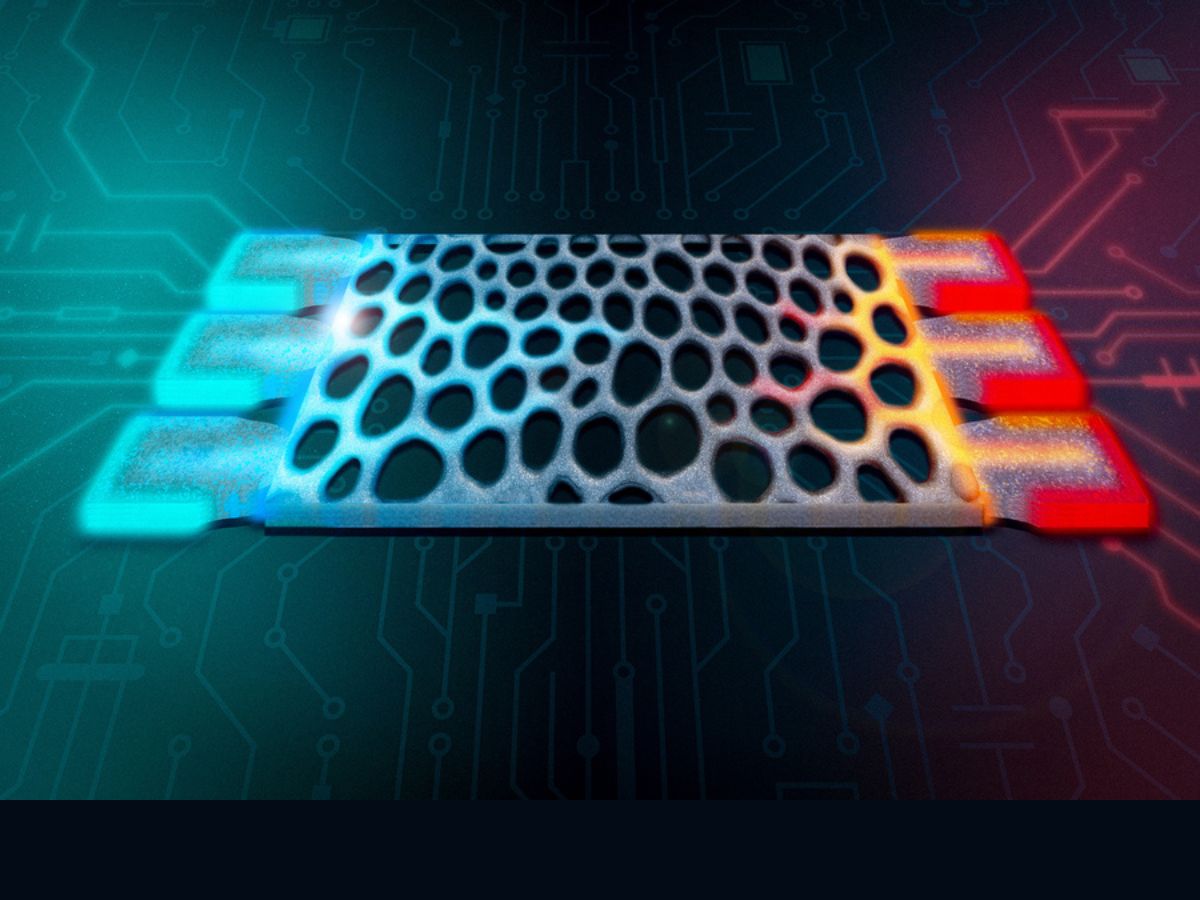
Engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have developed innovative silicon structures that convert waste heat into usable computing power. This groundbreaking advancement could significantly enhance energy efficiency in computing systems, addressing a key challenge in the technology sector.
The research, published in the APS Journals in March 2024, focuses on harnessing heat that is typically lost during computing processes. According to the team, the new silicon structures can effectively capture this waste heat and convert it into electrical energy, which can then be utilized to power various computing tasks.
The potential applications for this technology are vast. By integrating these silicon structures into existing computing frameworks, organizations could reduce energy consumption and lower operational costs. With growing concerns over energy efficiency and sustainability in technology, this development represents a significant step forward.
Innovative Approaches to Energy Use
The concept of converting waste heat into usable energy is not new, but MIT’s approach is particularly noteworthy. The researchers utilized advanced materials and engineering techniques to create silicon structures that improve the efficiency of heat conversion. During testing, the new system demonstrated a remarkable capability to generate power from thermal energy, achieving conversion efficiencies that exceed current technologies.
This research is part of a broader effort at MIT to explore sustainable energy solutions. The team’s findings could pave the way for future innovations that make computing less reliant on traditional power sources. As global demand for computing power continues to rise, finding sustainable energy alternatives becomes increasingly critical.
The implications extend beyond energy savings. By enhancing the efficiency of computing systems, organizations could also contribute to reducing their carbon footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals. This aligns well with initiatives aimed at promoting greener technologies in various sectors.
Future Prospects and Industry Impact
As the technology matures, there is potential for commercialization. Companies in the tech industry may soon adopt these silicon structures to enhance their systems. The drive towards energy-efficient computing is particularly relevant in data centers and cloud computing environments, where energy consumption is a significant concern.
The research at MIT represents a collaboration between different departments, showcasing the university’s commitment to interdisciplinary approaches in solving complex problems. By combining expertise in material science, engineering, and computing, the team has made strides that could affect a wide array of industries.
Further studies are planned to refine the technology and explore additional applications. As researchers continue to innovate, the dream of harnessing waste heat for computing power may soon become a reality in everyday technology.
In conclusion, MIT’s breakthrough in converting waste heat into computing power not only addresses immediate energy efficiency concerns but also sets the stage for a more sustainable future in technology. The potential for significant industry impact underscores the importance of continued investment in research and development in this field.