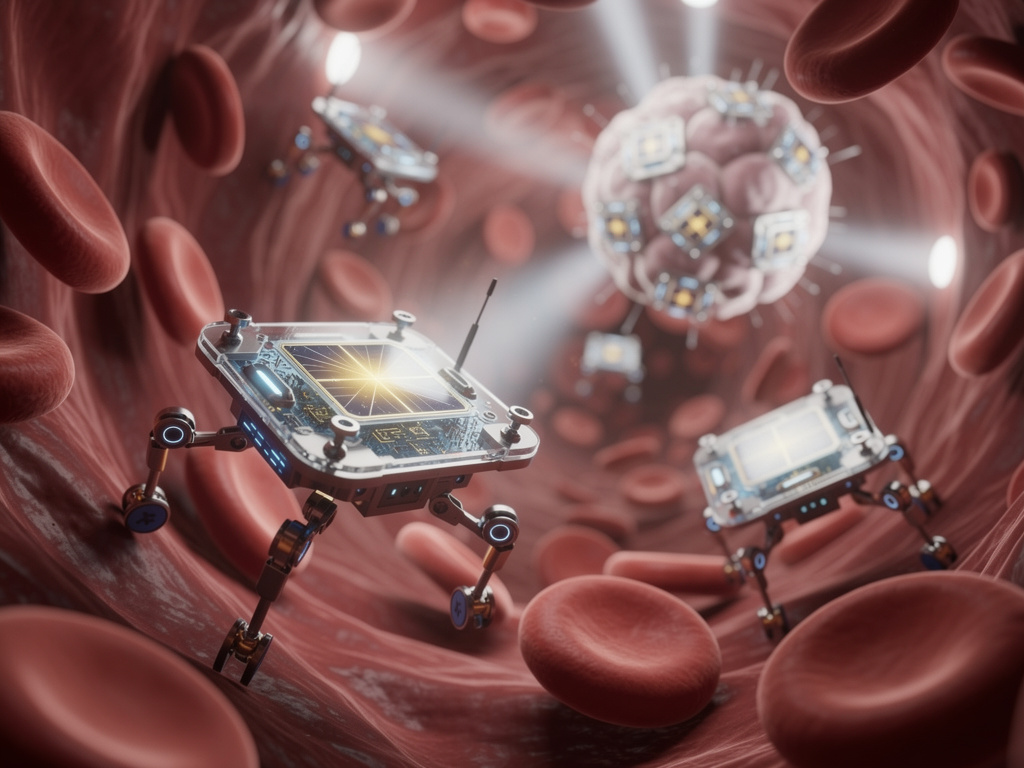
A revolutionary breakthrough in medical technology has emerged with the development of microscopic robots capable of navigating the human body. These minuscule devices, smaller than a grain of salt, are equipped with advanced features such as onboard computers, solar cells for energy, and propulsion systems that allow them to sense their environment. This innovation, detailed in a report by Futurism, signifies a potential transformation in diagnostics and treatment, paving the way for targeted therapies with minimal invasiveness.
The design of these robots is inspired by natural microorganisms, enabling them to traverse blood vessels and delicate tissues with remarkable precision. Researchers envision deploying swarms of these tiny robots to deliver treatments directly to cancer cells, significantly improving the effectiveness of therapies like chemotherapy. This approach could also facilitate real-time monitoring of internal conditions, reducing the need for surgical interventions.
Advancements in Microrobotics
The propulsion mechanisms of these robots often utilize magnetic fields or ultrasound waves, mimicking the movement of bacteria. Initial prototypes have demonstrated their ability to navigate simulated human environments successfully, avoiding obstacles and adapting to changing conditions. For patients suffering from chronic illnesses, such as interstitial cystitis, these robots could provide targeted medication delivery, minimizing side effects associated with broader systemic treatments.
Engineers at the University of Colorado Boulder have developed microrobots that are significantly smaller than a human hair, showcasing their potential to precisely target various medical conditions. This innovation may lead to shorter recovery times and reduced hospital stays, heralding a shift towards less invasive medical procedures.
Building these robots involves cutting-edge nanotechnology, where components are assembled at an atomic level. The onboard computer processes environmental data in real-time, making autonomous decisions regarding navigation and task execution. Solar cells can harvest energy from light sources, including biocompatible illumination within the body, allowing the devices to operate independently for extended periods.
Challenges remain in ensuring biocompatibility to avoid adverse immune responses, as well as refining control systems for safe operation. As highlighted by NIH News in Health, the range of medical robots is expanding, with applications from surgical assistance to these microscopic explorers. Enhancing capabilities through artificial intelligence could enable predictive analytics for early disease detection.
Potential Applications and Future Directions
In oncology, these robots could revolutionize cancer treatment by identifying and neutralizing tumors at their earliest stages. A scenario could involve a device that detects abnormal cell growth, administers therapeutic agents, and transmits data wirelessly, all without requiring any incisions. Insights from Hopkins EP Online emphasize how robotics is advancing healthcare innovations and preparing engineers for these emerging challenges.
Beyond oncology, the applications extend to neurology, where tiny implants using micro-LEDs can send light-based messages to the brain. This technology offers potential pathways for treating conditions like Parkinson’s disease or epilepsy, allowing for innovative rehabilitation methods. Furthermore, in cardiovascular health, these robots could clear blockages or deliver stents with precision, significantly reducing risks linked to current catheter-based procedures.
Despite the promise of these technologies, several regulatory and technical barriers must be overcome before widespread deployment. Ensuring safety through rigorous clinical trials is critical, as any malfunction within the body could have severe consequences. Developers are exploring biodegradable materials that dissolve harmlessly post-mission, mitigating long-term risks.
International efforts are accelerating progress, particularly in countries like Japan, where an aging population is driving innovation in dementia care through robotic aids. While these initiatives may not directly involve microrobots, they complement the development of technology that integrates AI for elder care.
As discussions on platforms like X highlight, the potential for these microrobots raises ethical questions regarding data privacy and long-term implications. Industry insiders emphasize the need for a balance between innovation and safeguards to ensure equitable access to these advancements across different socioeconomic backgrounds.
Looking ahead, combining microrobots with gene editing tools like CRISPR could enable targeted genetic repairs, addressing hereditary diseases at their source. Current prototypes have shown promise in tissue repair capabilities, while ongoing research is tackling challenges related to energy efficiency and navigation in dynamic environments.
As adoption of these technologies grows, the economic impacts on healthcare systems could be significant. The potential for preventive interventions may shift the focus from treatment to maintenance, resulting in lower healthcare costs. Industry analysts predict a multibillion-dollar market driven by aging populations and rising rates of chronic diseases.
The emergence of body-traversing robots marks a pivotal moment in medical history. From the groundbreaking device reported by Futurism to the broader integrations discussed in various sources, these innovations offer hope for resolving some of the most challenging issues in medicine today. With continued research and development, the line between science fiction and reality continues to blur, promising a healthier, more resilient future for humanity.