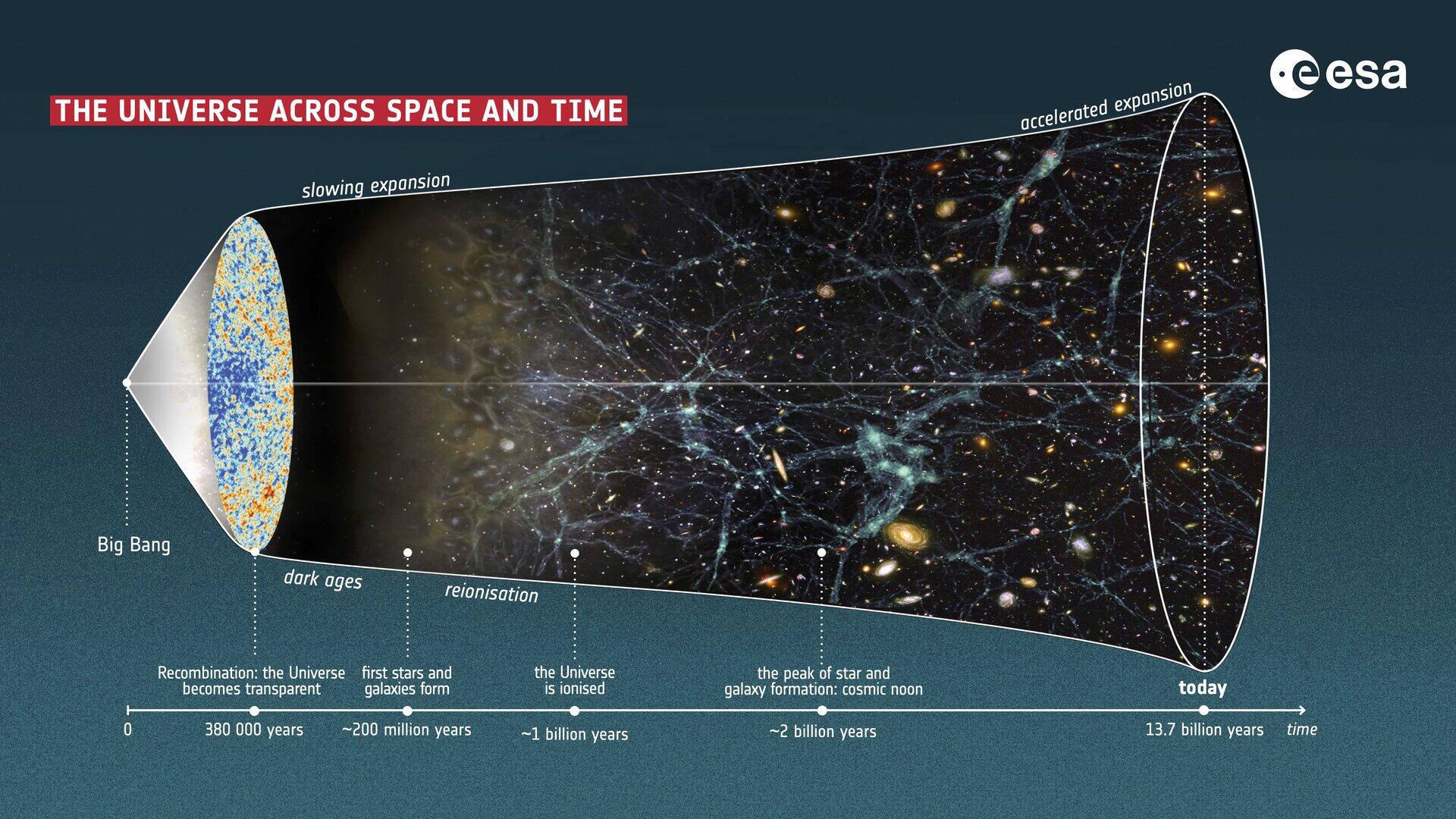
Recent research led by a team of astronomers suggests that the universe is currently experiencing a phase of decelerated expansion. This finding challenges long-standing assumptions about dark energy, which has been thought to drive the universe’s accelerated growth since its discovery approximately 27 years ago.
The study, conducted by researchers at Yonsei University in South Korea, examines what is known as the “Hubble residual.” This term refers to the difference between the observed distance of galaxies and their expected distances based on the current model of universal expansion. The authors of the study argue that strong statistical evidence supports their claim that the universe has slowed down in its expansion rate.
Significant Findings in Cosmology
According to lead researcher Professor Young-Wook Lee, the implications of this research could lead to a significant paradigm shift in cosmology. “Our study shows that the universe has already entered a phase of decelerated expansion at the present epoch and that dark energy evolves with time much more rapidly than previously thought,” he stated.
The research challenges the existing framework of cosmological theories, which have predominantly emphasized a universe that is continuously accelerating. If validated, these findings could reshape our understanding of cosmic evolution and the fundamental forces at play.
Future Research and Implications
The research team is now focused on further validating their results through additional observations and analyses. The implications of confirming a decelerated expansion could lead to new theories regarding the nature and behavior of dark energy.
The study highlights the dynamic nature of cosmological research, where new findings can lead to reevaluations of long-held beliefs. As scientists continue to explore the mysteries of the universe, this research underscores the importance of ongoing inquiry and the potential for groundbreaking discoveries.
The full details of the study have been published in reputable scientific journals, providing a platform for further academic discussion and exploration in the field of cosmology.