The latest report from Sophos, titled the State of Ransomware in Healthcare 2025, reveals critical shifts in the landscape of cyber threats facing healthcare organizations. For the first time in three years, exploited vulnerabilities have emerged as the leading technical cause of ransomware attacks, accounting for 33% of incidents. This report is based on data collected from 292 healthcare providers and highlights an industry grappling with evolving threats and increased pressure on IT teams.
Root Causes Emerge in Cybersecurity Landscape
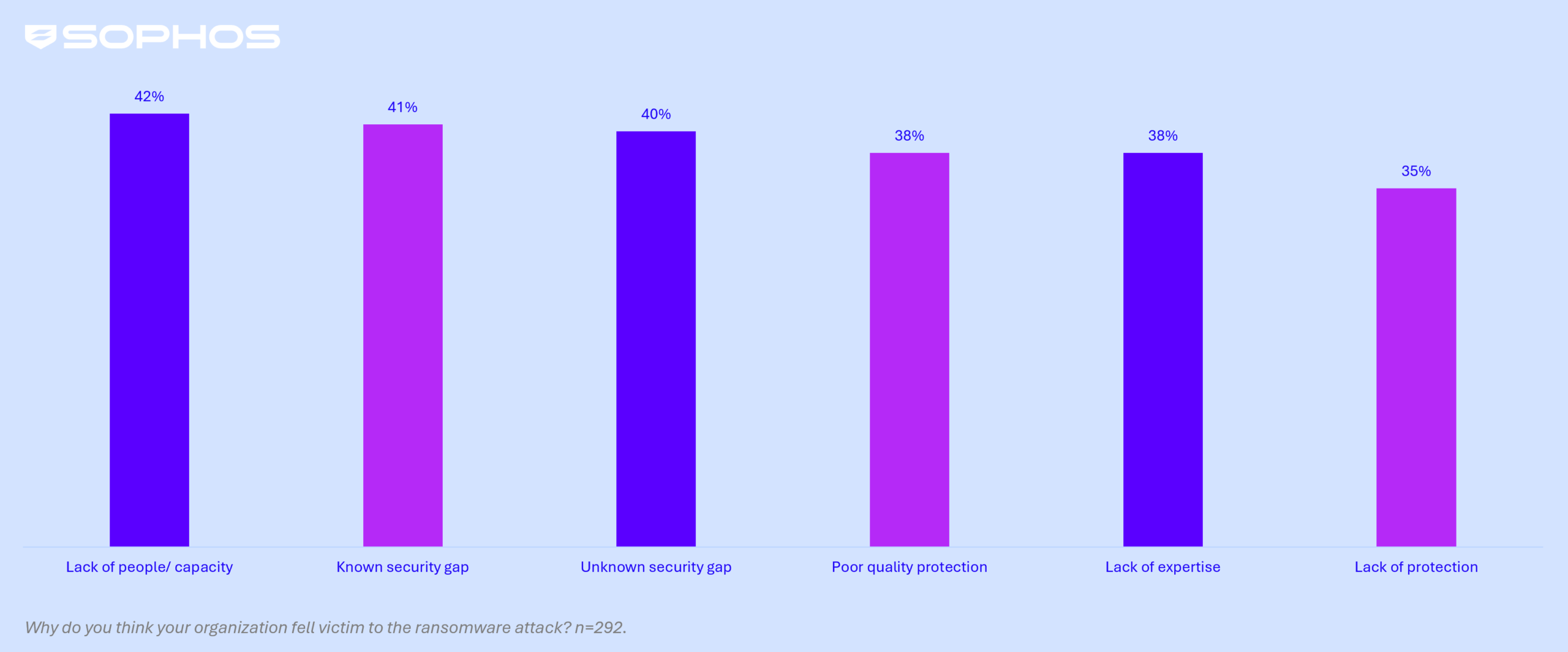
The report indicates a significant change in both technical and organizational factors contributing to ransomware attacks. The top organizational issue identified was a lack of personnel capacity, with 42% of respondents citing a shortage of cybersecurity experts monitoring their systems. This was closely followed by known security gaps, acknowledged by 41% of the organizations, which indicates weaknesses that had not been addressed prior to the attacks.
Shifting Dynamics in Ransomware Tactics
While healthcare providers have made strides in enhancing their defenses against data encryption, attackers are adapting their methods. The data encryption rate has notably dropped to its lowest level in five years, with only 34% of attacks resulting in data encryption, a significant decline from a peak of 74% in 2024. Concurrently, extortion-only attacks, where data is stolen without being encrypted, have tripled, now representing 12% of all incidents in 2025.
The financial dynamics of ransomware in healthcare have also changed dramatically. The average ransom demand has decreased by 91%, falling from $4 million in 2024 to just $343,000 this year. Similarly, the average ransom payment has dropped to $150,000, the lowest reported across all industries surveyed. The mean recovery cost, excluding ransom, has fallen by 60%, now standing at $1.02 million, down from $2.57 million in 2024.
The report underscores the human impact of these attacks, particularly on IT and cybersecurity teams within healthcare organizations. A substantial 39% of respondents reported increased pressure from senior leadership following a breach, while 37% experienced heightened anxiety regarding future attacks.
Despite the improved recovery speed—where 58% of healthcare providers reported recovering within a week in 2025, compared to just 21% in 2024—there are concerns regarding the use of backups. The reliance on backups for data recovery has declined to 51%, down from 72% in 2022, suggesting potential weaknesses in backup strategies.
The findings from Sophos serve as a critical reminder of the ongoing challenges within the healthcare sector regarding cybersecurity. As ransomware threats evolve, the need for robust defenses and adequate staffing becomes increasingly apparent.