BREAKING NEWS: Researchers from the University of Macau and Huazhong University of Science and Technology have unveiled a groundbreaking innovation in aquatic robotics: the leaf-inspired “S-aquabots.” These untethered robots, powered by a revolutionary Marangoni motor, promise to transform environmental monitoring and pollution control. The study detailing this development was published online in eScience in May 2025.
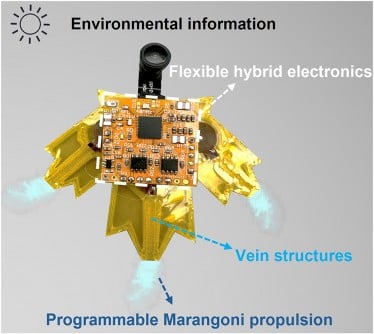
These centimeter-scale aquabots leverage the natural Marangoni effect, allowing for silent and energy-efficient propulsion using just 1.2 mL of ethanol. This remarkable design enables the S-aquabots to navigate up to 5 meters for approximately 226 seconds, outperforming traditional aquatic robots by improving fuel efficiency by 3.5 times.
The S-aquabots are equipped with advanced features allowing them to perform tasks such as obstacle avoidance, pollutant collection, and real-time video transmission. Their leaf-like structure not only provides camouflage among floating vegetation but also ensures their movement is nearly silent, registering at just 40 dB, comparable to natural background noise. This stealth makes them ideal for ecological monitoring without disturbing wildlife.
Prof. Junwen Zhong, the lead researcher, emphasized the significance of this advancement:
“Our leaf-inspired S-aquabots demonstrate how biomimicry and advanced materials can overcome the long-standing challenges of aquatic robotics. The quiet motion and natural camouflage open possibilities for unobtrusive environmental monitoring.”
These developments are crucial for addressing urgent environmental concerns. With the ability to gather data on water quality, track pollutants, and monitor weather conditions over extended periods, S-aquabots represent a major leap forward for both scientific research and disaster response efforts. Their precise maneuverability also positions them as valuable tools in search-and-rescue operations.
Looking ahead, integrating sustainable energy sources, such as solar cells, could further enhance the endurance of these innovative aquatic robots. The potential applications are vast, from environmental protection to scientific exploration and emergency response.
This research is supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund of Macau SAR, among other funding sources, highlighting the collaborative effort to advance this technology. As the world faces increasing environmental challenges, the S-aquabots could pave the way for smarter, more adaptable, and eco-friendly solutions in aquatic robotics.
Stay tuned for more updates as these revolutionary S-aquabots make waves in the field of environmental technology.