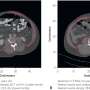
A recent study from the Mayo Clinic reveals that artificial intelligence (AI) can assess abdominal muscle density through imaging techniques to identify adults at a higher risk of falling, beginning in midlife. Published in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings, this research emphasizes the role of abdominal muscle quality as a significant factor in predicting fall risk for individuals aged 45 years and older.
The study highlights that maintaining strong abdominal muscles contributes to core strength, which is essential for physical stability. As people age, the loss of muscle mass and quality can lead to diminished balance and an increased likelihood of falls. By leveraging AI technology, researchers can analyze imaging data to provide insights into muscle density, offering a proactive approach to fall prevention.
Understanding the Connection Between Muscle Density and Falls
The findings indicate that individuals with lower abdominal muscle density may need targeted interventions to enhance their core strength. As falls can lead to severe injuries, particularly in older adults, this predictive capability is crucial. The Mayo Clinic study provides a framework for healthcare professionals to assess risk factors more accurately.
Incorporating AI into this process allows for more personalized health recommendations, enabling individuals to make informed choices about their physical activity and strength training routines. This research underscores the potential for AI to transform preventative healthcare strategies, especially for an aging population.
Implications for Future Research and Healthcare Practices
The implications of the study extend beyond individual assessments. As healthcare systems worldwide grapple with the challenges of an aging demographic, understanding the factors that contribute to falls is vital. The integration of AI in medical imaging not only enhances the accuracy of assessments but also paves the way for innovative solutions in fall prevention.
Going forward, further research will be necessary to refine these AI models and explore their applicability in various healthcare settings. This study lays the groundwork for future investigations that may incorporate additional variables such as lifestyle, nutrition, and overall fitness levels.
As communities seek effective methods to improve elderly care and reduce fall-related injuries, the findings from the Mayo Clinic serve as a timely reminder of the intersection between technology and health. By focusing on muscle quality and employing advanced imaging analysis, there is potential to significantly impact public health initiatives aimed at enhancing the quality of life for older adults.