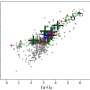
Astronomers using the Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) have made a significant discovery regarding the nearby galactic globular cluster known as NGC 6569. Their observations reveal that this cluster is actively losing stars due to a process called tidal stripping. These findings were published on December 22, 2023, on the arXiv preprint server, underscoring the dynamic nature of this celestial body.
Understanding the mechanisms behind star loss is crucial for astrophysics. Tidal stripping occurs when the gravitational forces exerted by a larger galaxy pull stars away from a smaller cluster. In the case of NGC 6569, the cluster’s proximity to its host galaxy allows for this star loss to be observed more readily. The AAT’s detailed observations provide a clearer picture of how such interactions influence the evolution of globular clusters.
Implications of Star Loss in NGC 6569
The implications of the findings extend beyond the immediate observations. NGC 6569 is one of many globular clusters that populate galaxies, and understanding its star dynamics can offer insights into the fate of similar structures in the universe. Researchers are keenly interested in how tidal interactions affect stellar populations, as these processes can lead to significant changes in the cluster’s overall mass and composition.
Astronomers have long studied globular clusters for their ancient stars, which are believed to contain valuable information about the early universe. The loss of stars from NGC 6569 may not only alter its mass but also influence the formation of new stars in the vicinity. This ongoing research highlights the interconnectedness of galactic structures and the importance of monitoring such celestial phenomena.
Future Research Directions
Moving forward, astronomers plan to conduct further studies to quantify the rate of star loss in NGC 6569 and explore the effects of its interactions with nearby galaxies. By employing advanced observational techniques and instruments, including future upgrades to the AAT, scientists hope to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the processes at play.
The research surrounding NGC 6569 serves as a reminder of the complexities involved in stellar evolution and the dynamic nature of galaxies. As astronomers continue to investigate these phenomena, they bring us closer to unraveling the mysteries of the universe and understanding the life cycles of stars within various galactic environments.
In summary, the observations of NGC 6569 represent a significant advancement in our knowledge of globular clusters and their interactions. The study of these cosmic structures not only informs us about their current state but also sheds light on the broader mechanisms that govern the universe’s evolution.