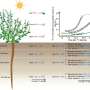
Research conducted by a team led by Prof. Zeng Fanjiang from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has unveiled a significant mechanism that enhances soil carbon sinks in arid regions. The findings, published in the journal New Phytologist on November 23, 2023, highlight the crucial role of desert microbes in promoting carbon storage within these challenging ecosystems.
The study indicates that microbial activity in arid soils is essential for carbon sequestration, which is vital for mitigating climate change. The researchers focused on understanding how specific microbial pathways contribute to the accumulation of soil organic carbon. Their findings suggest that these microbes not only aid in carbon storage but also enhance soil health, making it a key area for future environmental conservation efforts.
Understanding the interaction between microbes and soil carbon dynamics can provide insights into how agricultural practices might be adjusted to improve soil quality and carbon retention. The research emphasizes that promoting microbial diversity could lead to more resilient ecosystems capable of storing greater amounts of carbon, thus playing a role in climate regulation.
The implications of this study extend beyond theoretical knowledge; they hold practical significance for land management strategies in arid regions worldwide. By enhancing microbial pathways, it may be possible to develop approaches that increase soil carbon sinks, which can contribute to global efforts in combating climate change.
As climate change continues to pose significant challenges, findings such as these underscore the importance of understanding the biological processes that govern carbon storage in soils. The work of Prof. Zeng’s team offers a promising avenue for future research aimed at harnessing microbial activity to bolster soil carbon reserves, ultimately benefiting both the environment and agricultural productivity.
Overall, this research not only advances scientific understanding but also reinforces the need for sustainable practices that leverage natural processes to combat climate change effectively.